8. Asset Pricing: The Lucas Asset Pricing Model#
GPU
This lecture was built using a machine with access to a GPU — although it will also run without one.
Google Colab has a free tier with GPUs that you can access as follows:
Click on the “play” icon top right
Select Colab
Set the runtime environment to include a GPU
8.1. Overview#
An asset is a claim on a stream of prospective payments.
What is the correct price to pay for such a claim?
The asset pricing model of Lucas [Lucas, 1978] attempts to answer this question in an equilibrium setting with risk-averse agents.
Lucas’ model provides a beautiful illustration of model building in general and equilibrium pricing in competitive models in particular.
In this lecture we work through the Lucas model and show where the fundamental asset pricing equation comes from.
We’ll write code in both Numba and JAX.
Since the model is relatively small, the speed gain from using JAX is not as large as it is in some other lectures.
Nonetheless, the gain is nontrivial.
Let’s start with some imports:
import jax.numpy as jnp
import jax
import numpy as np
import numba
from scipy.stats import lognorm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from time import time
8.2. The Lucas Model#
Lucas studied a pure exchange economy with a representative consumer (or household), where
Pure exchange means that all endowments are exogenous.
Representative consumer means that either
there is a single consumer (sometimes also referred to as a household), or
all consumers have identical endowments and preferences
Either way, the assumption of a representative agent means that prices adjust to eradicate desires to trade.
This makes it very easy to compute competitive equilibrium prices.
8.2.1. Basic Setup#
Let’s review the setup.
8.2.1.1. Assets#
There is a single “productive unit” that costlessly generates a sequence of consumption goods \(\{y_t\}_{t=0}^{\infty}\).
Another way to view \(\{y_t\}_{t=0}^{\infty}\) is as a consumption endowment for this economy.
We will assume that this endowment is Markovian, following the exogenous process
Here \(\{ \xi_t \}\) is an IID shock sequence with known distribution \(\phi\) and \(y_t \geq 0\).
An asset is a claim on all or part of this endowment stream.
The consumption goods \(\{y_t\}_{t=0}^{\infty}\) are nonstorable, so holding assets is the only way to transfer wealth into the future.
For the purposes of intuition, it’s common to think of the productive unit as a “tree” that produces fruit.
Based on this idea, a “Lucas tree” is a claim on the consumption endowment.
8.2.1.2. Consumers#
A representative consumer ranks consumption streams \(\{c_t\}\) according to the time separable utility functional
Here
\(\beta \in (0,1)\) is a fixed discount factor.
\(u\) is a strictly increasing, strictly concave, continuously differentiable period utility function.
\(\mathbb{E}\) is a mathematical expectation.
8.2.2. Pricing a Lucas Tree#
What is an appropriate price for a claim on the consumption endowment?
We’ll price an ex-dividend claim, meaning that
the seller retains this period’s dividend
the buyer pays \(p_t\) today to purchase a claim on
\(y_{t+1}\) and
the right to sell the claim tomorrow at price \(p_{t+1}\)
Since this is a competitive model, the first step is to pin down consumer behavior, taking prices as given.
Next, we’ll impose equilibrium constraints and try to back out prices.
In the consumer problem, the consumer’s control variable is the share \(\pi_t\) of the claim held in each period.
Thus, the consumer problem is to maximize (8.1) subject to
along with \(c_t \geq 0\) and \(0 \leq \pi_t \leq 1\) at each \(t\).
The decision to hold share \(\pi_t\) is actually made at time \(t-1\).
But this value is inherited as a state variable at time \(t\), which explains the choice of subscript.
8.2.2.1. The Dynamic Program#
We can write the consumer problem as a dynamic programming problem.
Our first observation is that prices depend on current information, and current information is really just the endowment process up until the current period.
In fact, the endowment process is Markovian, so that the only relevant information is the current state \(y \in \mathbb R_+\) (dropping the time subscript).
This leads us to guess an equilibrium where price is a function \(p\) of \(y\).
Remarks on the solution method
Since this is a competitive (read: price taking) model, the consumer will take this function \(p\) as given.
In this way, we determine consumer behavior given \(p\) and then use equilibrium conditions to recover \(p\).
This is the standard way to solve competitive equilibrium models.
Using the assumption that price is a given function \(p\) of \(y\), we write the value function and constraint as
subject to
We can invoke the fact that utility is increasing to claim equality in (8.2) and hence eliminate the constraint, obtaining
The solution to this dynamic programming problem is an optimal policy expressing either \(\pi'\) or \(c\) as a function of the state \((\pi, y)\).
Each one determines the other, since \(c(\pi, y) = \pi (y + p(y))- \pi' (\pi, y) p(y)\)
8.2.2.2. Next Steps#
What we need to do now is determine equilibrium prices.
It seems that to obtain these, we will have to
Solve this two-dimensional dynamic programming problem for the optimal policy.
Impose equilibrium constraints.
Solve out for the price function \(p(y)\) directly.
However, as Lucas showed, there is a related but more straightforward way to do this.
8.2.2.3. Equilibrium Constraints#
Since the consumption good is not storable, in equilibrium we must have \(c_t = y_t\) for all \(t\).
In addition, since there is one representative consumer (alternatively, since all consumers are identical), there should be no trade in equilibrium.
In particular, the representative consumer owns the whole tree in every period, so \(\pi_t = 1\) for all \(t\).
Prices must adjust to satisfy these two constraints.
8.2.2.4. The Equilibrium Price Function#
Now observe that the first-order condition for (8.3) can be written as
where \(v'_1\) is the derivative of \(v\) with respect to its first argument.
To obtain \(v'_1\) we can simply differentiate the right-hand side of (8.3) with respect to \(\pi\), yielding
Next, we impose the equilibrium constraints while combining the last two equations to get
In sequential rather than functional notation, we can also write this as
This is the famous consumption-based asset pricing equation.
Before discussing it further we want to solve out for prices.
8.2.3. Solving the Model#
Equation (8.4) is a functional equation in the unknown function \(p\).
The solution is an equilibrium price function \(p^*\).
Let’s look at how to obtain it.
8.2.3.1. Setting up the Problem#
Instead of solving for it directly we’ll follow Lucas’ indirect approach, first setting
so that (8.4) becomes
Here \(h(y) := \beta \int u'[G(y, z)] G(y, z) \phi(dz)\) is a function that depends only on the primitives.
Equation (8.7) is a functional equation in \(f\).
The plan is to solve out for \(f\) and convert back to \(p\) via (8.6).
To solve (8.7) we’ll use a standard method: convert it to a fixed point problem.
First, we introduce the operator \(T\) mapping \(f\) into \(Tf\) as defined by
In what follows, we refer to \(T\) as the Lucas operator.
The reason we do this is that a solution to (8.7) now corresponds to a function \(f^*\) satisfying \((Tf^*)(y) = f^*(y)\) for all \(y\).
In other words, a solution is a fixed point of \(T\).
This means that we can use fixed point theory to obtain and compute the solution.
8.2.3.2. A Little Fixed Point Theory#
Let \(cb\mathbb{R}_+\) be the set of continuous bounded functions \(f \colon \mathbb{R}_+ \to \mathbb{R}_+\).
We now show that
\(T\) has exactly one fixed point \(f^*\) in \(cb\mathbb{R}_+\).
For any \(f \in cb\mathbb{R}_+\), the sequence \(T^k f\) converges uniformly to \(f^*\).
Note
If you find the mathematics heavy going you can take 1–2 as given and skip to the next section
Recall the Banach contraction mapping theorem.
It tells us that the previous statements will be true if we can find an \(\alpha < 1\) such that
Here \(\|h\| := \sup_{x \in \mathbb{R}_+} |h(x)|\).
To see that (8.9) is valid, pick any \(f,g \in cb\mathbb{R}_+\) and any \(y \in \mathbb{R}_+\).
Observe that, since integrals get larger when absolute values are moved to the inside,
Since the right-hand side is an upper bound, taking the sup over all \(y\) on the left-hand side gives (8.9) with \(\alpha := \beta\).
8.3. Computation#
The preceding discussion tells that we can compute \(f^*\) by picking any arbitrary \(f \in cb\mathbb{R}_+\) and then iterating with \(T\).
The equilibrium price function \(p^*\) can then be recovered by \(p^*(y) = f^*(y) / u'(y)\).
Let’s try this when \(\ln y_{t+1} = \alpha \ln y_t + \sigma \epsilon_{t+1}\) where \(\{\epsilon_t\}\) is IID and standard normal.
Utility will take the isoelastic form \(u(c) = c^{1-\gamma}/(1-\gamma)\), where \(\gamma > 0\) is the coefficient of relative risk aversion.
We’ll use Monte Carlo to compute the integral
Monte Carlo is not always the fastest method for computing low-dimensional integrals, but it is extremely flexible (for example, it’s straightforward to change the underlying state process).
8.3.1. Numba Code#
Let’s start with code using NumPy / Numba (and then compare it to code using JAX).
We create a function that returns tuples containing parameters and arrays needed for computation.
def create_lucas_tree_model(γ=2, # CRRA utility parameter
β=0.95, # Discount factor
α=0.90, # Correlation coefficient
σ=0.1, # Volatility coefficient
grid_size=500,
draw_size=1_000,
seed=11):
# Set the grid interval to contain most of the mass of the
# stationary distribution of the consumption endowment
ssd = σ / np.sqrt(1 - α**2)
grid_min, grid_max = np.exp(-4 * ssd), np.exp(4 * ssd)
grid = np.linspace(grid_min, grid_max, grid_size)
# Set up distribution for shocks
np.random.seed(seed)
ϕ = lognorm(σ)
draws = ϕ.rvs(500)
# And the vector h
h = np.empty(grid_size)
for i, y in enumerate(grid):
h[i] = β * np.mean((y**α * draws)**(1 - γ))
# Pack and return
params = γ, β, α, σ
arrays = grid, draws, h
return params, arrays
Here’s a Numba-jitted version of the Lucas operator
@numba.jit
def T(params, arrays, f):
"""
The Lucas pricing operator.
"""
# Unpack
γ, β, α, σ = params
grid, draws, h = arrays
# Turn f into a function
Af = lambda x: np.interp(x, grid, f)
# Compute Tf and return
Tf = np.empty_like(f)
# Apply the T operator to f using Monte Carlo integration
for i in range(len(grid)):
y = grid[i]
Tf[i] = h[i] + β * np.mean(Af(y**α * draws))
return Tf
To solve the model, we write a function that iterates using the Lucas operator to find the fixed point.
def solve_model(params, arrays, tol=1e-6, max_iter=500):
"""
Compute the equilibrium price function.
"""
# Unpack
γ, β, α, σ = params
grid, draws, h = arrays
# Set up and loop
i = 0
f = np.ones_like(grid) # Initial guess of f
error = tol + 1
while error > tol and i < max_iter:
Tf = T(params, arrays, f)
error = np.max(np.abs(Tf - f))
f = Tf
i += 1
price = f * grid**γ # Back out price vector
return price
Let’s solve the model and plot the resulting price function
params, arrays = create_lucas_tree_model()
γ, β, α, σ = params
grid, draws, h = arrays
# Solve once to compile
start = time()
price_vals = solve_model(params, arrays)
numba_with_compile_time = time() - start
print("Numba compile plus execution time = ", numba_with_compile_time)
Numba compile plus execution time = 5.768648624420166
# Now time execution without compile time
start = time()
price_vals = solve_model(params, arrays)
numba_without_compile_time = time() - start
print("Numba execution time = ", numba_without_compile_time)
Numba execution time = 4.151984214782715
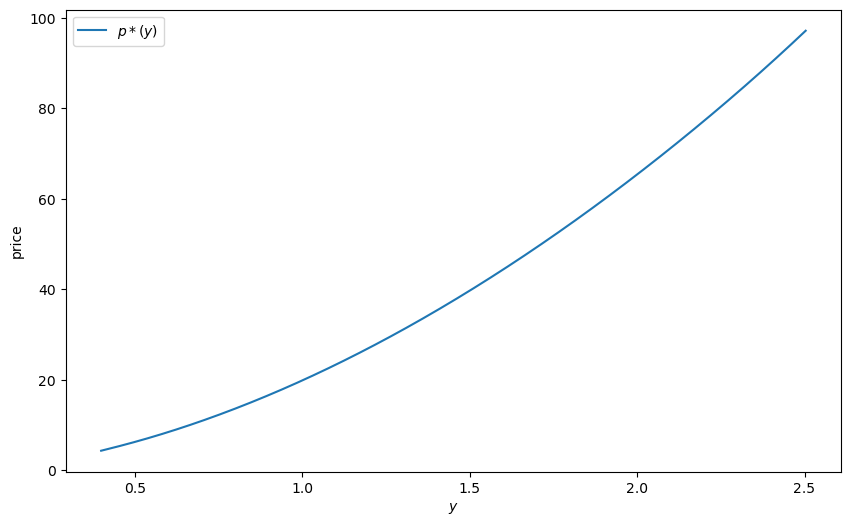
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
ax.plot(grid, price_vals, label='$p*(y)$')
ax.set_xlabel('$y$')
ax.set_ylabel('price')
ax.legend()
plt.show()
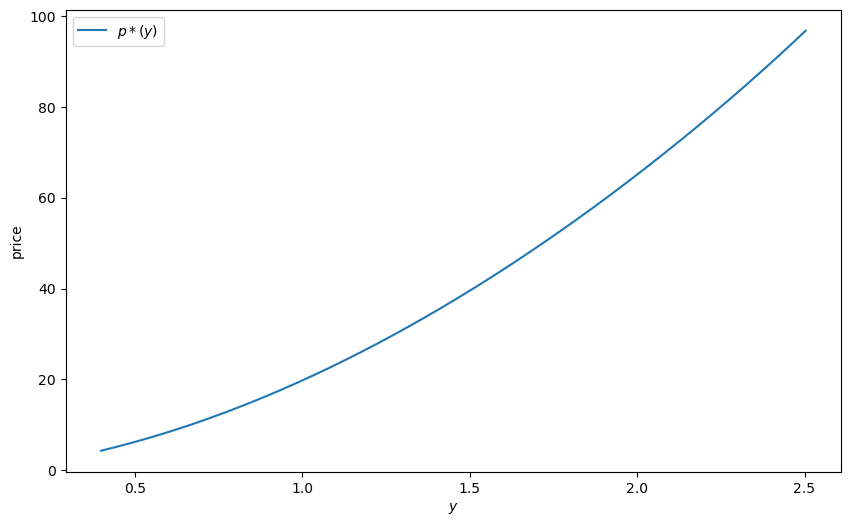
We see that the price is increasing, even if we remove all serial correlation from the endowment process.
The reason is that a larger current endowment reduces current marginal utility.
The price must therefore rise to induce the household to consume the entire endowment (and hence satisfy the resource constraint).
8.3.2. JAX Code#
Here’s a JAX version of the same problem.
def create_lucas_tree_model(γ=2, # CRRA utility parameter
β=0.95, # Discount factor
α=0.90, # Correlation coefficient
σ=0.1, # Volatility coefficient
grid_size=500,
draw_size=1_000,
seed=11):
# Set the grid interval to contain most of the mass of the
# stationary distribution of the consumption endowment
ssd = σ / jnp.sqrt(1 - α**2)
grid_min, grid_max = jnp.exp(-4 * ssd), jnp.exp(4 * ssd)
grid = jnp.linspace(grid_min, grid_max, grid_size)
# Set up distribution for shocks
key = jax.random.key(seed)
draws = jax.random.lognormal(key, σ, shape=(draw_size,))
grid_reshaped = grid.reshape((grid_size, 1))
draws_reshaped = draws.reshape((-1, draw_size))
h = β * jnp.mean((grid_reshaped**α * draws_reshaped) ** (1-γ), axis=1)
params = γ, β, α, σ
arrays = grid, draws, h
return params, arrays
We’ll use the following function to simultaneously compute the expectation
over all \(y\) in the grid, under the current specifications.
@jax.jit
def compute_expectation(y, α, draws, grid, f):
return jnp.mean(jnp.interp(y**α * draws, grid, f))
# Vectorize over y
compute_expectation = jax.vmap(compute_expectation,
in_axes=(0, None, None, None, None))
Here’s the Lucas operator
@jax.jit
def T(params, arrays, f):
"""
The Lucas operator
"""
grid, draws, h = arrays
γ, β, α, σ = params
mci = compute_expectation(grid, α, draws, grid, f)
return h + β * mci
We’ll use successive approximation to compute the fixed point.
def successive_approx_jax(T, # Operator (callable)
x_0, # Initial condition
tol=1e-6 , # Error tolerance
max_iter=10_000): # Max iteration bound
def body_fun(k_x_err):
k, x, error = k_x_err
x_new = T(x)
error = jnp.max(jnp.abs(x_new - x))
return k + 1, x_new, error
def cond_fun(k_x_err):
k, x, error = k_x_err
return jnp.logical_and(error > tol, k < max_iter)
k, x, error = jax.lax.while_loop(cond_fun, body_fun,
(1, x_0, tol + 1))
return x
successive_approx_jax = \
jax.jit(successive_approx_jax, static_argnums=(0,))
Here’s a function that solves the model
def solve_model(params, arrays, tol=1e-6, max_iter=500):
"""
Compute the equilibrium price function.
"""
# Simplify notation
grid, draws, h = arrays
γ, β, α, σ = params
_T = lambda f: T(params, arrays, f)
f = jnp.ones_like(grid) # Initial guess of f
f = successive_approx_jax(_T, f, tol=tol, max_iter=max_iter)
price = f * grid**γ # Back out price vector
return price
Now let’s solve the model again and compare timing
params, arrays = create_lucas_tree_model()
grid, draws, h = arrays
γ, β, α, σ = params
# Solve once to compile
start = time()
price_vals = solve_model(params, arrays).block_until_ready()
jax_with_compile_time = time() - start
print("JAX compile plus execution time = ", jax_with_compile_time)
JAX compile plus execution time = 0.9894521236419678
# Now time execution without compile time
start = time()
price_vals = solve_model(params, arrays).block_until_ready()
jax_without_compile_time = time() - start
print("JAX execution time = ", jax_without_compile_time)
print("Speedup factor = ", numba_without_compile_time/jax_without_compile_time)
JAX execution time = 0.5730574131011963
Speedup factor = 7.245319787966019
Let’s check the solutions are similar
8.4. Exercises#
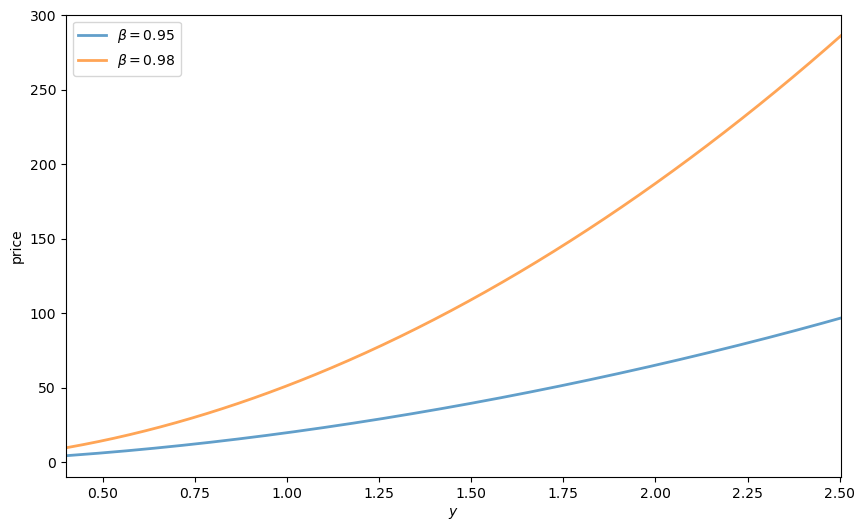
Exercise 8.1
When consumers are more patient the asset becomes more valuable, and the price of the Lucas tree shifts up.
Show this by plotting the price function for the Lucas tree when \(\beta = 0.95\) and \(0.98\).
Solution
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
for β in (.95, 0.98):
params, arrays = create_lucas_tree_model(β=β)
grid, draws, h = arrays
γ, beta, α, σ = params
price_vals = solve_model(params, arrays)
label = rf'$\beta = {beta}$'
ax.plot(grid, price_vals, lw=2, alpha=0.7, label=label)
ax.legend(loc='upper left')
ax.set(xlabel='$y$', ylabel='price', xlim=(min(grid), max(grid)))
plt.show()